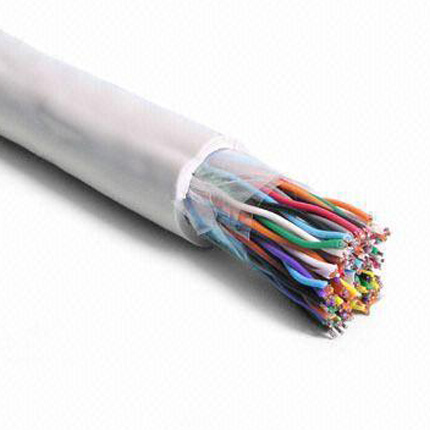
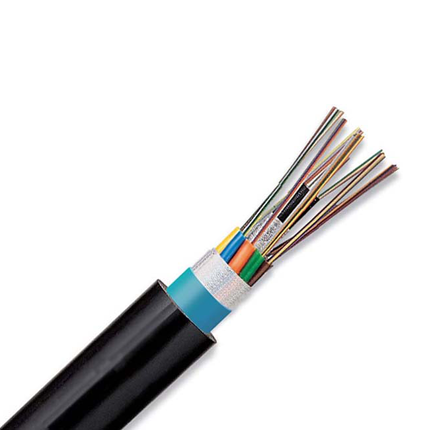
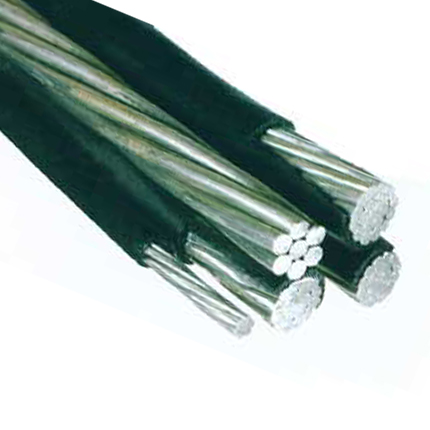
Polyethylene exhibits:
- Excellent electrical insulating properties
- Good stable mechanical properties
- Resistance to chemical attacks
All these properties have rendered polyethylene an efffective and important insulating material in the manufacture of low volage cables. Polyethylene is however not suitable for use under high temperatures. This is mainly due to the molecular structure of the polyethylene polymer which is made up of ethylene monomers loosely held together by weak molecular bonds. This (and other reasons) led to the development of associated compounds, such as
MDPE (Medium-density polyethylene) - It is a type of polyethylene defined by a density range of 0.926–0.940 g/cm3. It is less dense than HDPE, which is more common. It can be produced by chromium/silica catalysts, Ziegler-Natta catalysts or metallocene catalysts. MDPE has good shock and drop resistance properties. It also is less notch sensitive than HDPE. Stress cracking resistance is better than that of HDPE. MDPE is typically used in gas pipes and fittings, sacks, shrink film, packaging film, carrier bags, and screw closures. It has good heat deformation properties. Its melt temp. is above 120°C. It has good abrasion resistance, low water permability and low coefficient of friction. It is well suited for insulation and cable jacketing of power cables. It can resist severe laying condition.